Mitosis/체세포분열 — IB Biology
Unit/Course: 1.6의 일부분
SL/HL: SL과 HL 모두
중요도: 5/5
서론/나의 의견 (접은글)
체세포분열 단원은 1단원중 가장 어려운 단원이 아닌가 싶다.
처음 배울때는 이것 저것 외울게 많다고 느껴지겠지만, 시간이 지나고 다른 단원을 배우다 보면 자동으로 학습되어있는 자신을 보게 될 것이다.
즉, 처음에는 좀 짜증나고 귀찮은 단원인건 인정.
참고로 Mitosis는 시험에서 큰 배점으로 나오지는 않는듯 하다. 하지만, Paper 2에 Short answer로 2점정도 짜리 문제로 잘 나온다. 특히, SL은 더 자주 나오는 것 같기도...?
그러니까 시간이 많은 1 학기때 Mitosis를 마스터 하자.
참고로, Mitosis만 공부하면 망한다. 꼭 Cell cycle, 암의 발달과정, Cyclin과 같은 녀석을 공부하자. 이 녀석들 은근히 많이 나온다.
언젠간 Cell cycle에 관한 글을 쓰겠다. 어렵지 않지만 햇갈려 하는 친구들을 많이 봤다. Cell cycle 햇갈리면 Mitosis도 햇갈리니, 꼭 Cell cycle에 관한 내용을 숙지하고 공부하자.
본론
Mitosis는 한마디로 '한 개의 세포가 두 개가 됨!' 이다.
Mitosis의 과정을 알아야 한다. Mitosis는 Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase의 순서로 진행된다.
이 과정들의 첫 글자를 모아 PMAT으로 외워버리자.
참고로, Prokaryotes (원핵생물)은 Binary Fission (이분법)으로 분열한다. 애초에 얘네들은 세포 하나로 이루어진 생물임으로, 이분법으로 분열하면 1 마리였던 원핵생물이 2 마리가 된다. TMI를 쓰자면, binary fission 때문에 박테리아가 무서운거다. Binarry fission으로 분열하는 것을 n으로 놓는다면, 2^n의 개체수가 나온다. Binary fission 10 번씩 하면 박테리아 1 마리가 1024 마리가 되는거다.
Mitosis의 의미는 무엇일까? 개체의 수리와 성장이 Mitosis의 의미다.
만약 생물이 다치면 세포가 죽거나 파손되는데, mitosis를 통해 새로운 세포를 만들어서 죽은 세포를 대체한다. 즉, 세포를 수리하기 위해서. 또, 성장한다는것은 세포가 더 많이 필요하다는 것이니, Mitosis가 필요하다.
하지만, Mitosis는 체세포 (Somatic cell)에만 적용된다. 생식세포 (Zygotes)는 3단원에서 배울 Meiosis를 통해 생성된다.
1 단원에 나오지는 않지만, Mitosis는 SA:V ratio (표면적:부피 비율)을 높히기 위해서 필요하기도 하다. 더 알고싶으면 접은글 처리한 설명을 클릭해서 보도록.
Surface Area:Volume Ratio는 표면적대 부피 비율을 나타낸다. 세포가 막무가내로 커지기만 하면, 부피가 크는 속도가 표면적이 커지는 속도보다 빠르기 때문에, SA:V ratio가 낮아진다. 이렇게 되면, 세포는 열 배출이나 노폐물 배출에 걸리는 속도가 더 들고, 효율적이지 못하게 된다. 그래서 특정 크기가 된다면 mitosis를 통해 SA:V ratio를 낮추어 주어야 한다. (굳이 비유하자면... 사과를 반으로 쪼개면 표면적:부피 비율이 낮아진다는 점...?)
다시 말하지만, 이거 모르거나 이해가 안되도 당연한거다. SA:V에 관한건 어차피 2 단원 (맞나..?)에서 나온다. 그때 공부하면 된다.
자, 이제 Mitosis의 과정에 대해 알아보자.
Prophase 에서는....
1. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus degenerates.
— 핵막과 인이 없어진다.
2. DNA supercoils, and chromosomes become visible.
— DNA가 Supercoil 되기 때문에, 현미경으로 염색체가 관찰 가능하다.
— Supercoil의 디테일은 1 단원에서 알지 않다도 된다. 하지만 어짜피 알아야 하는 내용이니, 궁금하다면 접은글을 클릭해서 보자.
DNA는 Interphase (간기)에서 가느다란 실 형태인 염색사로 존재한다. 이 '실'들이 뭉침으로써 염색체를 형성하고, 현미경으로 관찰된다.
이해가 안된다면, 실을 생각하자. 실 한 가닥은 얇아서 잘 안보이지만, 실을 뭉쳐서 털뭉치를 만든다면 두꺼워져서 보기 쉽다.
3. Centrosomes move to the opposite poles of the cell. Spindle fiber is formed.
— Centrosome (중심체)가 세포의 양 극으로 이동한다. 한마디로, 중심체가 서로 다른 방향으로 움직이고 spindle fiber (방추사)가 형성된다.
Metaphase 에서는....
1. Spindle fiber from both centrosome connect to the centromere of the chromosome.
— 말 장난에 조심하자. Centrosome은 중심체, Centromere는 염색체의 중간 부분을 말한다.
2. The chromosomes align along the equitorial plane.
— 세포 중간에 염색체들이 질서있게 나열된다.
— 염색체들이 질서있게 나열되어 있기 때문에, 염색체를 관찰하기 딱 좋은 시기이다.
Anaphase 에서는....
1. Spindle fiber shortens, pulling the identical sister chromatids to each side.
— Mitosis의 염색체는 S 기를 거쳤기 때문에 chromatids 두 개로 이루어진 염색체를 가지고 있다. 이 염색분체들이 담고 있는 유전적 정보는 동일하다.
Telophase 에서는....
1. Nuclear membrane starts regenerating near each chromatids.
— 각 염색분체 주변으로 핵막이 생기기 시작함.
2. Chromosome starts to decondense.
— 염색체의 농축이 풀려서 눈에 보이지 않게 됨.
3. Cytokinesis occurs
— 사이토키네시스가 일어남. 사이토키네시스는 한 개의 세포가 두 개로 나누어짐.
...
...
...
이해가 잘 안됐을 것이다. 특히, Anaphase하고 Telophase에서 염색체와 염색분체의 개념이 햇갈릴 것이다.
염색체와 염색분체의 개념이 햇갈린다면, 접은글을 클릭해서 개념을 확실히 잡고 가자.
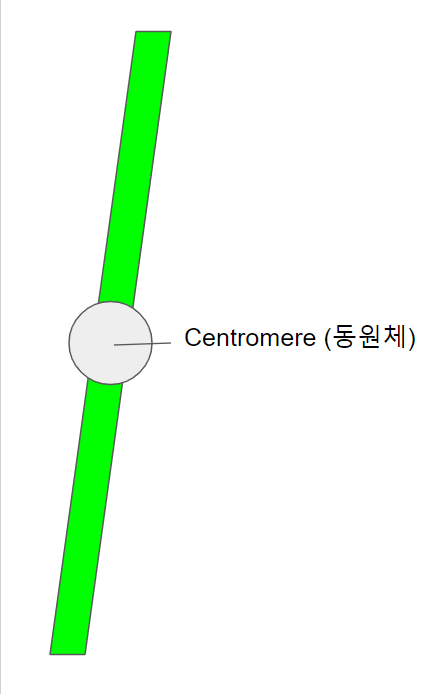
지금이라도 디지털 미술을 하면 유명해질것 같은 나의 그림을 보자. 위에 있는 그림은 S phase를 거치지 않은 chromosome (염색체)다.
저 그림에서 초록색 부분을 유전 정보라고 가정하자.
S phase에서 DNA가 복제된다는것은 알고 있겠지? (모르면 Cell cycle 먼저 공부하자.)
S phase에서 DNA가 복제되면 초록색 부분이 두배가 된다는 뜻이다. 그래서, S phase를 거친 염색체는 아래에 그림처럼 된다.
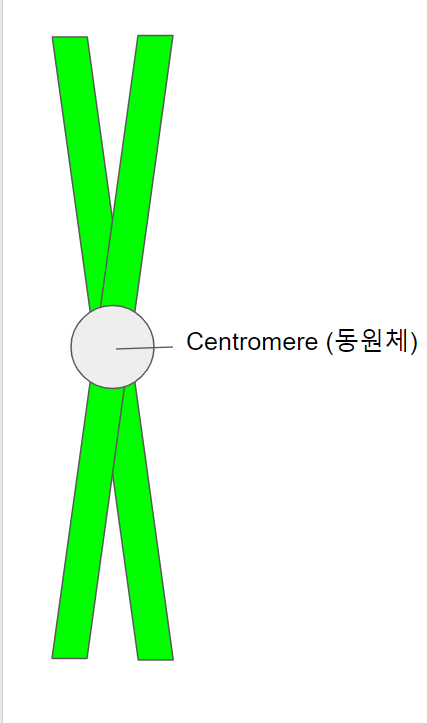
아까 그림과는 달리, DNA를 나타내는 연두색 부분이 두 배로 늘어났다. 즉, DNA가 Ctrl+C, Ctrl+V 되었다. 하지만, 염색체는 아직 1 개이다. 염색체는 동원체 (centromere)의 갯수로 센다고 외우는게 정신건강에 이롭다. 즉, 아까 그림과 지금 그림은 회색 동그라미로 그려진 동원체가 1 개임으로 염색체의 갯수는 늘어나지 않았지만, 연두색으로 그려진 DNA의 양만 늘어났다.
여러분은 아마 "그럼 네가 아까 말한 chromatid (염색분체)는 뭔데?"라고 물어볼 것 같다.
염색 분체는 S phase를 거친 염색체에서만 존재한다.
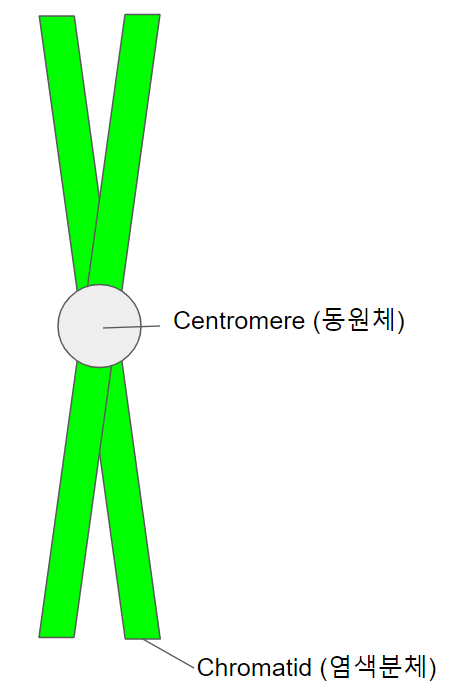
그림 3에 보여진 것 처럼 염색분체 (Chromatid)는 염색체를 이루고 있는 초록색 부분 한 개를 말한다.
쉽게 말하면, S phase를 거치지 않은 염색체는 염색분체가 1 개 있는 염색체이다. S phase를 거친 염색체는 염색분체가 2 개 있는 염색체이다.
Anaphase에서 염색분체가 반으로 분리된다. 염색분체가 반으로 분리되면 염색분체는 각각 동원체를 가지기 때문에, 새로운 세포의 염색체 수는 본래 세포의 염색체 수와 같게 된다. (새로운 세포의 염색체는 그림 1의 모양이랑 같다).
참고로 centromere (동원체) 현미경으로 안보이니, 그림을 가지고 학습한 후 현미경 사진을 보면서 공부하자. 현미경 사진 많이 나오니까 꼭 공부해야 한다!!
내가 Google Slide로 그린 아름답고 멋진 그림으로 알아보자. (...)
G1 phase:

G1 phase의 세포가 이렇게 생겼다는것을 기억하자. 아, 참고로 G1기에 chromosome은 보이지 않을 뿐더러, 저렇게 생기지 않았다! 주의하자. 이때 chromosome은 chromatin (염색사)로 존재하는데, 그냥 실처럼 생겼고 너무 얇아서 현미경으로 보이지 않는다.
S Phase를 거친 세포 (G2 Phase):

G1 phase와 비교했을때 DNA 양이 2 배로 늘었지만, 염색체 수는 똑같다는것을 명심하자. 염색체 수 = 동원체의 수.
(Number of chromosomes = Number of centromeres)
Prophase:

Prophase에서는 말했듯이 Chromosome이 보이고, Nuclear membrane이 없어지고, Centrosome이 양극으로 이동한다. 염색체가 가지고 있는
Metaphase:

Metaphase에서는 spindle fiber가 chromosome의 centromere (염색체의 회색부분)에 붙는다. 또, 염색체가 equitorial plane에 나열된다.
Anaphase:

Anaphase에서 염색체 1 개를 구성하고 있었던 2 개의 chromatid (염색분체)가 분리되어 세포의 양 극으로 이동한다. 또, 염색분체가 분리되면서 염색체는 2 개가 된다.
Telophase:

Telophase과 동시에 cytokinesis (세포질분열)이 일어나는것을 묘사했다. Telophase와 cytokinesis 과정을 거친 세포는 어떻게 생겼냐하면...

'잠깐... 어디서 많이 본 것 같은데' 싶으면 맞게 생각한것이다. 그림 1.0, 즉 G1 phase를 나타낸 그림과 같다. 이제 이 세포는 G1, S, G2 phase를 거쳐서 또 분열할 것이다. (물론, 아예 분열을 안하는 G0기로 갈 수도 있지만...)
참고로, 세포의 대부분은 Interphase에서 시간을 보낸다. 이 세포가 미친듯이 계속 분열한다면, 그것은 암 세포이다.
....
....
....
이제, 내가 낸 문제를 보고 풀어보자. 답과 해설은 접은글 처리했으니, 답과 해설이 궁금하면 접은글을 클릭해서 보도록 하자. IB 처럼 영어로 내겠다! 사악한 웃음
Q1) Which of the following statement is true? (난이도: 2/5)
A. Via mitosis, organisms produce zygotes like sperm.
B. Via mitosis, organisms can repair damaged tissues.
C. Via mitosis, organisms can replicate its DNA.
D. There are four stages of mitosis: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telomerase.
Answer: B, as mitosis can be used to repiar damaged cell or for growth in general.
A: Organisms produce zygotes through meiosis, not mitosis.
C: Organisms replicate their DNA in S phase.
D: Four stages of mitosis are: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase, not telomearse.
TMI, 몰라도 됌: Telomerase is an reverse transcriptase enzyme that elongates the telomere in the chromosome.
근데, telophase는 telomere와 같은 단어들과 햇갈릴 수 있으니 잘 외워두자.
Q2) How does prokaryotic bacterium E.coli reproduce? (난이도: 2/5)
A. Mitosis
B. Meiosis
C. Binary fission
D. Sexual reproduction
Answer: C, as bacterium E.coli is a prokaryote and undergoes binary fission.
A: Prokaryotes undergo binary fission, which is basically mitosis, but you still have to know the exact term 'Binary fission' for prokaryotes.
B: Meiosis occurs only on eukaryotes.
D: Only soem eukaryotes reproduce sexually.
Q3)

The image above is a cell undergoing mitosis. Exactly which phase is the cell undergoing? (난이도: 4/5)
A. Prophase
B. Metaphase
C. Anaphase
D. Telophase
Answer: C, as it shows chromosomes (appears to be stained blue in this case) on both ends of the cell.
A: Prophase doesn't show chromosomes in both pole (or both ends) of the cell.
B: Metaphase shows chromosomes lined up in the middle (equitorial plane).
D: Telophase should show chromosomes that are arrived in both poles. This image seems like the chromosomes are still on the move.
Image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anaphase#/media/File:Anaphase_IF.jpg
Q4) Dave's cell is undergoing rapid cell cycle. Dave's stomach cells are undergoing mitosis every 5 hours, when regular people's stomach undergo mitosis once every 24 hours. Name Dave's medical condition. (Note: disregard other possibilities such as cellular damage or infection. Dave's condition is related to cell cycle.) (난이도: 3/5)
___________________________ (주관식)
A: (Stomach) cancer.
Cancer cells undergo mitosis and divides themselves very quickly, as it doesn't get stopped by the cell cycle regulators.
Q5) Describe the process of mitosis (객관식, 6 marks)
_________________________________ (주관식)
The answer should contain the following points to obtain a mark. Maximum mark: 6
1. Mitosis occurs on somatic cell only
2. Mitosis is used to repair damage or for growth
3. Mitosis occurs after Interphase (or G1, S, G2 phase)
4. Nuclear membrane/Nucleolus degenerates on prophase, and chromosome gets visible
5. Chromosomes align on the equatorial plane on metaphase.
6. Spindle fiber attatches to the centromere of the chromosomes in metaphase
7. Sister chromatids move to the each side of the pole in Anaphase,
8. Nuclear membrane/Nucleolus regenerates on telophase, and chromosomes start to uncoil.
9. Cytokinesis divides the cell.
Example answer:
Mitosis is a process where a cell divides into two. Mitosis occurs only on somatic cell. Mitosis' point is to repair or replace the damaged cell, or for general growth. Mitosis occurs after the interphase. During the interphase, the cell prepares for mitosis. Cell grows on G1 phase, DNA replicates on S phase, and cell synthesizes the protein required for division on G2 phase. After that, the cell enters mitosis. The cell undergoing mitosis goes through the processs of: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase in that order. During prophase, nuclear membrane degenerates along with nucleolus. Through supercoiling, chromosomes get visible under microscope. The cell moves on to metaphase, where the chromosome align on the equatorial plane. The spindle fibers from centrosomes attatch to the chromosome's centromere. The cell then moves to the anaphase, where the sister chromatids of a chromosomes are separated to each side of the pole. After that, telophase occurs, which regenerates the nuclear membrane and nucleolus. The cell's choromosomes starts to become invisible as they start to uncoil. Also, cytokinesis divides the cell, making one cell into two.